Language Model Resources
This page is basically a directory of links. I have a hodgepodge of useful bookmarks accumulated over time in a yet-to-be-well-organized bookmark directory and I wanted to group up a few of them for specific topics (this page being for links related to language model stuff). I figured I might as well post it here for my own reference and so others might get use from it! These links are not necessarily in any particular order, but I will try to provide a brief description each.
Intro to Language Models (LMs):
Two fantastic and comprehensive articles:
What We Know About LLMs (Primer)
Table of contents:

Getting Started with Large Language Models: Key Things to Know

Models, So Many Models:
The Rise and Rise of A.I. Large Language Models
Screenshot of the chart:
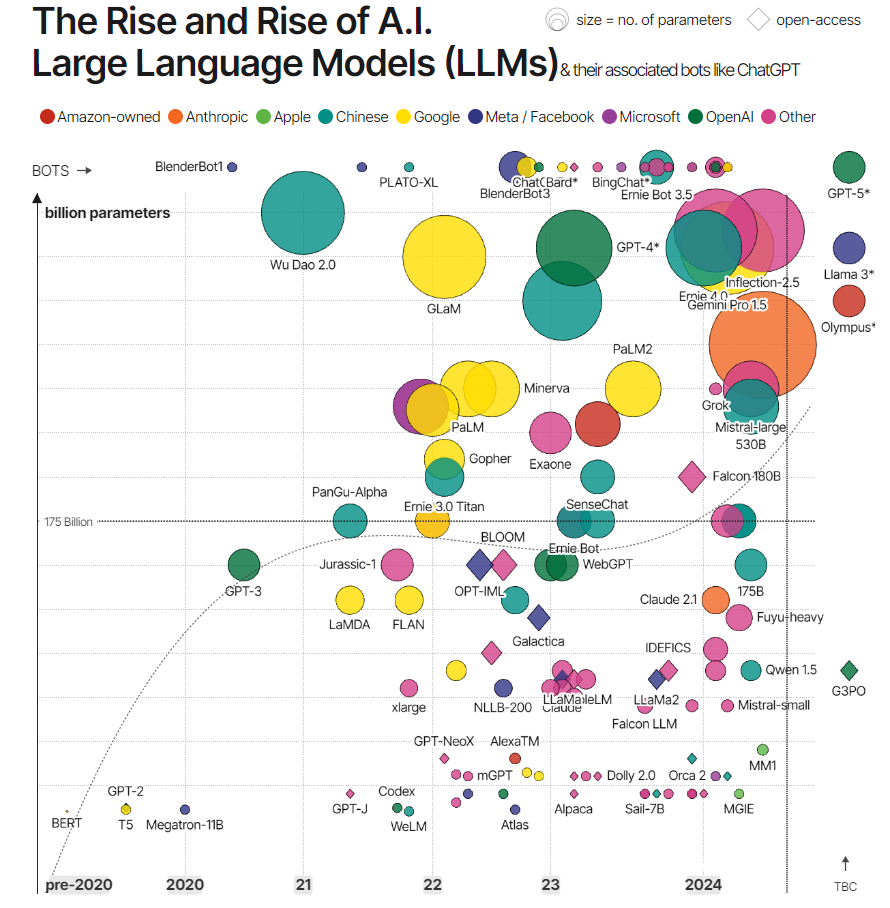
- Very cool chart visualizing data representing the explosion of various language models over the last 4 years or so.
- An article below the chart outlines a very interesting data story of the models developing over time.
LMSYS Chatbot Arena Leaderboard
- This is a crowdsourced open platform for LLM evals, and rankings based on performance.
LLM Explorer
- Really nicely organized lists, rankings, and categorizations of LLMs.
AI / ML / LLM / Transformer Models Timeline and List
- “This is a collection of important papers in the area of Large Language Models and Transformer Models. It focuses on recent development, especially from mid-2022 onwards”
- Cool graph/timeline
- The image is huge so it’s hard to show in screenshot, but:
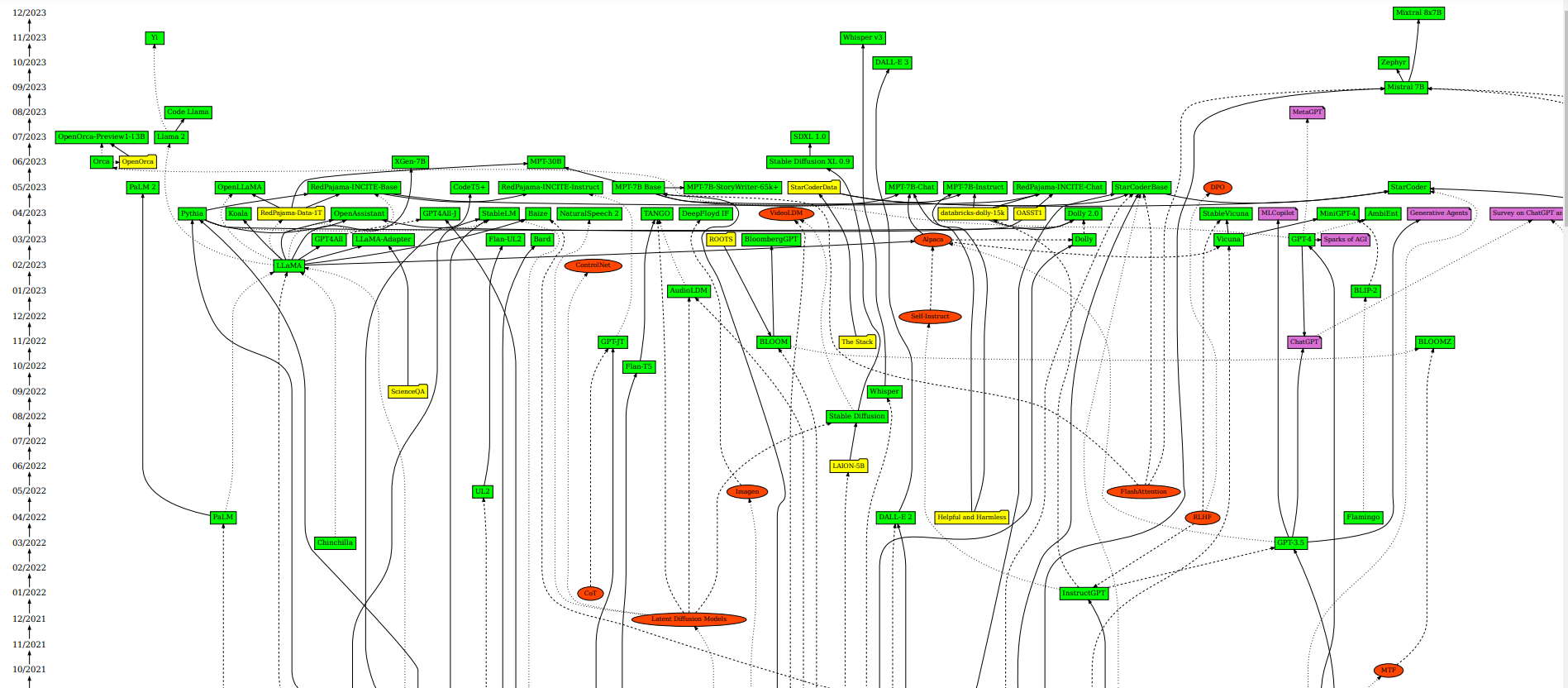
LMs’ Impact on Programming Paradigms:
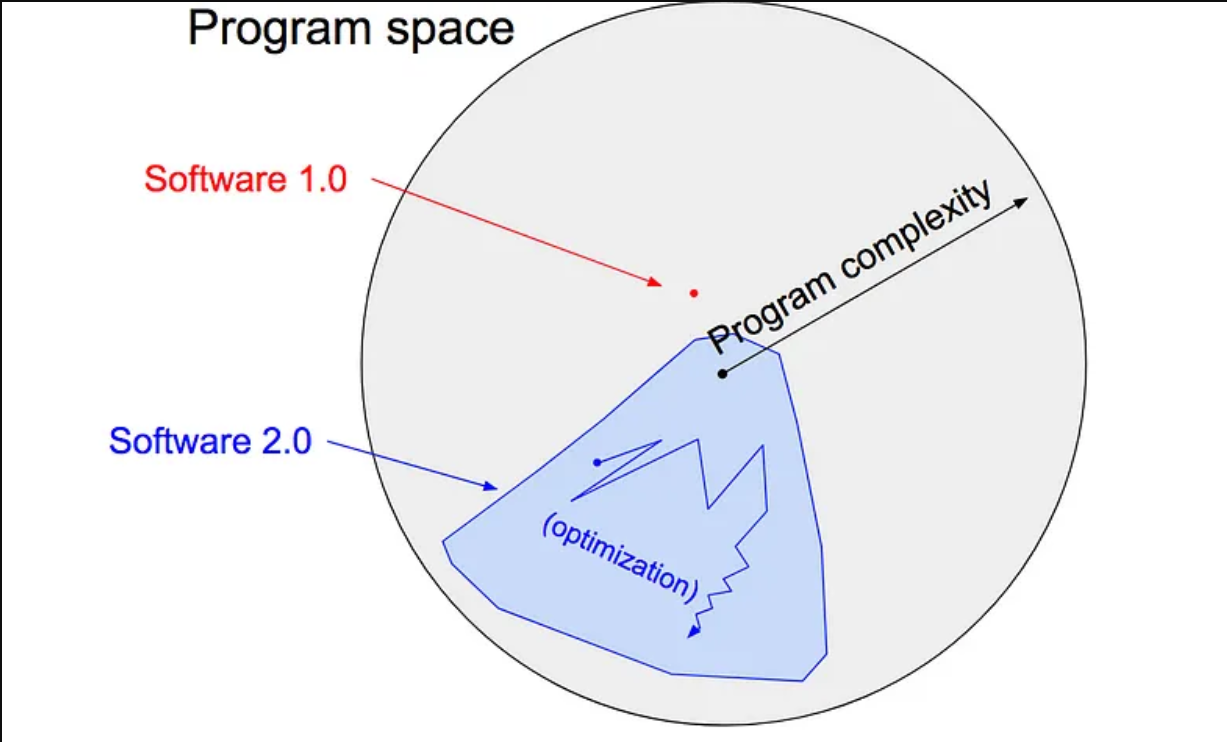
Software 2.0
- Pivotal article written by Andrej Karpathy in 2017.
- My summary won’t do it justice, but here:
- The article argues that neural networks signify a transformative shift from traditional “Software 1.0” to “Software 2.0.”
- Software 1.0 : Programmers write explicit instructions in code.
- Software 2.0 : relies on neural networks where behavior is defined by training on datasets rather than direct programming.
- This shift simplifies certain tasks, such as visual recognition and speech synthesis, by using neural networks to optimize and learn from large datasets instead of manually coding complex rules.
- Software 2.0 allows for more efficient and adaptable systems but comes with challenges like interpretability and vulnerability to biases. The article envisions that as Software 2.0 continues to evolve, it will impact various fields and require new development tools and practices tailored to its paradigm.
Software 1.0 vs 2.0 program space diagram:
- Final shoutout to Andrej for this fantastic “Intro to Large Language Models” video:
Deeper into the LM Landscape:
State of AI Report 2023
- Nathan Beniach’s annual “State of AI” report is a comprehensive analysis of the current landscape in artificial intelligence.
- Covers key advancements, industry trends, and emerging technologies in AI.
- Insights on AI research, market dynamics, policy implications, and major players in the field.
- Note: If you want to try to somehow keep up with the crazy pace of the LM/AI space, Nathan also puts out a monthly report on his substack.
- Similarly, to keep track of the “bleeding edge”, you might want to check out bleeding edge for “a feed of noteworthy developments in AI”.
AI Canon
- This article provides a curated collection of resources for understanding modern AI.
- Includes foundational papers, blog posts, courses, and guides, focusing on the transformative impact of technologies like transformers and latent diffusion models.
- Starts with overview of these technologies, progresses through technical learning resources and practical guides for building with large language models (LLMs), and concludes with landmark research, notably the 2017 paper “Attention is All You Need” that introduced transformer models.
(Almost) Everything I know about LLMs
- This article provides a comprehensive overview of Large Language Models (LLMs), focusing on their components, data flow, and evaluation methods.
- Emphasizes the importance of prompting techniques and the role of user feedback in improving model performance.
- Highlights various tools and techniques for fine-tuning and augmenting LLMs, aiming to offer a foundational understanding for those interested in the field.
Large language model Wikipedia page
- Very informative and consistently updated. It seems to be updated almost daily!
Research Papers:
“Attention is All You Need” Summary
- A summary of the landmark 2017 paper “Attention Is All You Need”
Reflexion: Language Agents with Verbal Reinforcement Learning
- Very interesting paper (published February 2024) on a new reinforcement learning method (potentially much more efficient than the human labor intensive RLHF (reinforcement learning from human feedback) standard method).
- From the abstract:
“We propose Reflexion, a novel framework to reinforce language agents not by updating weights, but instead through linguistic feedback. Concretely, Reflexion agents verbally reflect on task feedback signals, then maintain their own reflective text in an episodic memory buffer to induce better decision-making in subsequent trials. Reflexion is flexible enough to incorporate various types (scalar values or free-form language) and sources (external or internally simulated) of feedback signals, and obtains significant improvements over a baseline agent across diverse tasks (sequential decision-making, coding, language reasoning). For example, Reflexion achieves a 91% pass@1 accuracy on the HumanEval coding benchmark, surpassing the previous state-of-the-art GPT-4 that achieves 80%.”
Deeper Technical Understanding:
What Is ChatGPT Doing… and Why Does It Work?
- This article from Stephen Wolfram provides a high-level overview of how transformer based large language models generate human-like text by predicting the next word based on probabilities derived from vast amounts of text data.
- Explains the importance of randomness in producing creative and varied outputs and touches on the underlying neural network architecture and training process.
- Explains concepts like probability-based text generation, neural networks, and training processes in a way that is accessible to readers with a basic understanding of AI and machine learning.
Transformers from Scratch
- Transformer architecture is the basis for the largest and most capable language models as of August, 2024.
- A transformer is a deep learning architecture developed by researchers at Google and based on the multi-head attention mechanism, proposed in a 2017 paper “Attention Is All You Need”
- WARNING: This is a deep dive on transformers. Like the title implies, this dive is truly deep!
Scaling ChatGPT: Five Real-World Engineering Challenges
- The (scaling) challenges discussed within:
- KV Cache & GPU RAM
- Optimizing batch size
- Finding the right metrics to measure
- Finding GPUs wherever they are
- Inability to autoscale
Vector Databases A Technical Primer
- This is a pdf slide presentation for a Technical Primer on Vector Databases.
- As of August, 2024 the state of the art LLM tools largely are integrated with RAG (retrieval-augmented generation) systems. In this system, queries and documents are stored as vectors, and these vectors are stored in vector databases.
Other Random LM Resources:
AI Explained
- My favorite YouTube channel for news and analysis on AI/LM developments. Lot’s of channels constantly post fluff for views, but this channel seems to post more purposefully and respectably in terms of when videos are published and what is in them and how they are titled/thumbnailed.
bleeding edge
- “a feed of noteworthy developments in AI”
- This site has very cool/clean interactive timeline for said developments.
LAION (Large-scale Artificial Intelligence Open Network)
- LAION is a nonprofit, open source organization providing datasets, tools and models for machine learning research.
- Provides large, useful datasets!
EleutherAI
- EleutherAI is a nonprofit, open source AI research lab that focuses on interpretability and alignment of large models.
- Provides models, codebases, datasets, and lots of research done in the open!
LLM failure archive (ChatGPT and beyond)
- An interesting and useful GitHub.
- From the README:
A repo containing failure cases for ChatGPT and similar models, with the purpose of further study. I think it could be useful for:
- comparison with other models
- creation of synthetic data for testing and/or training